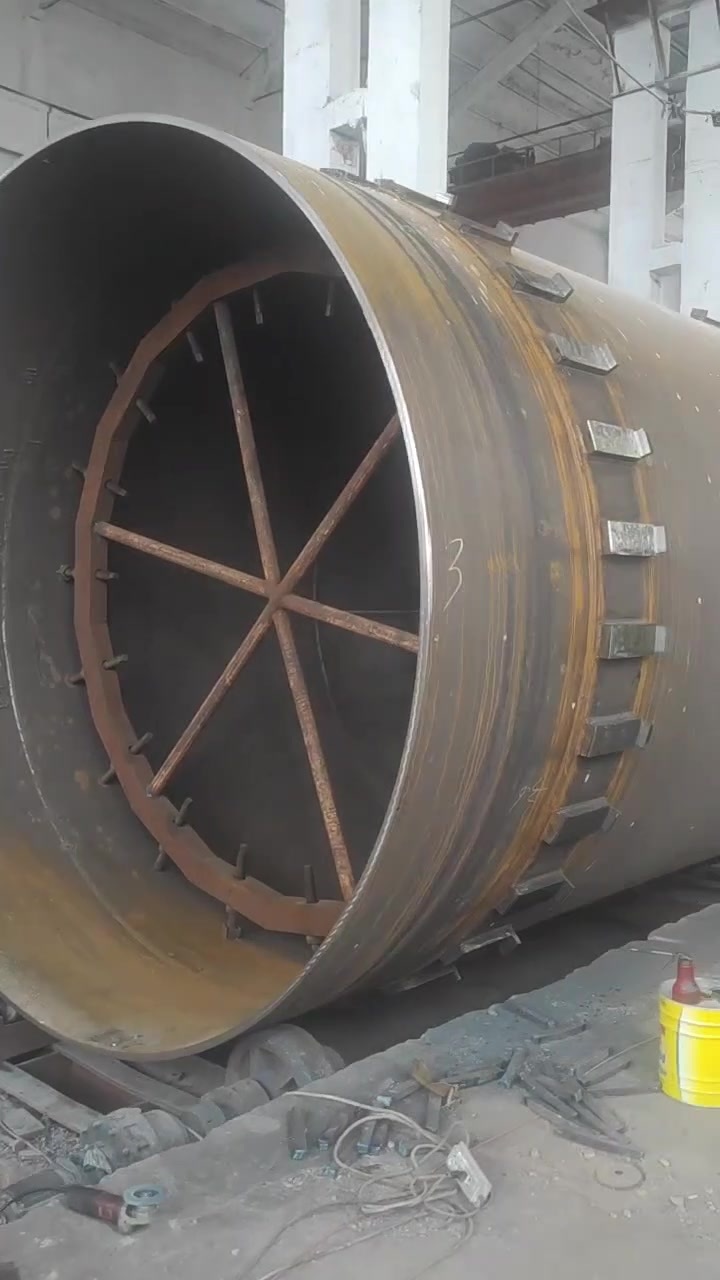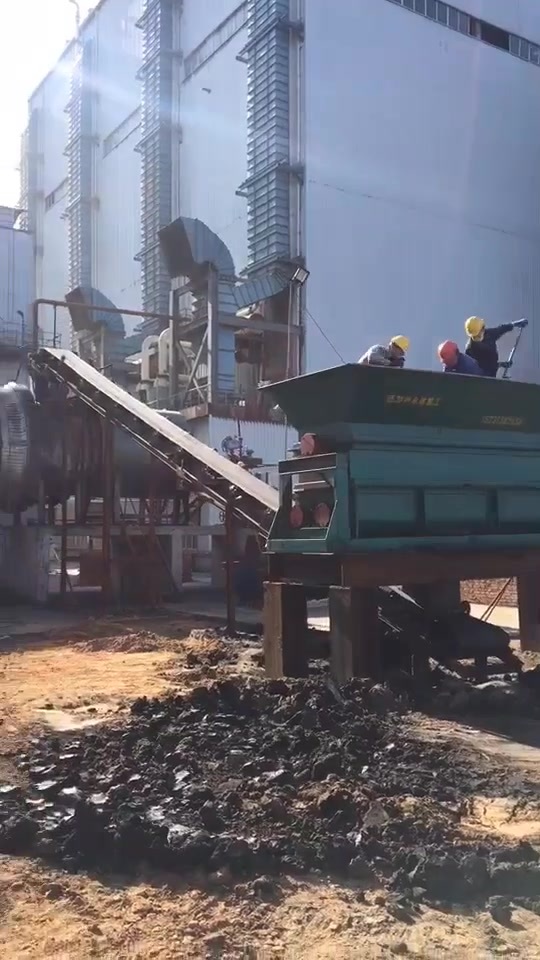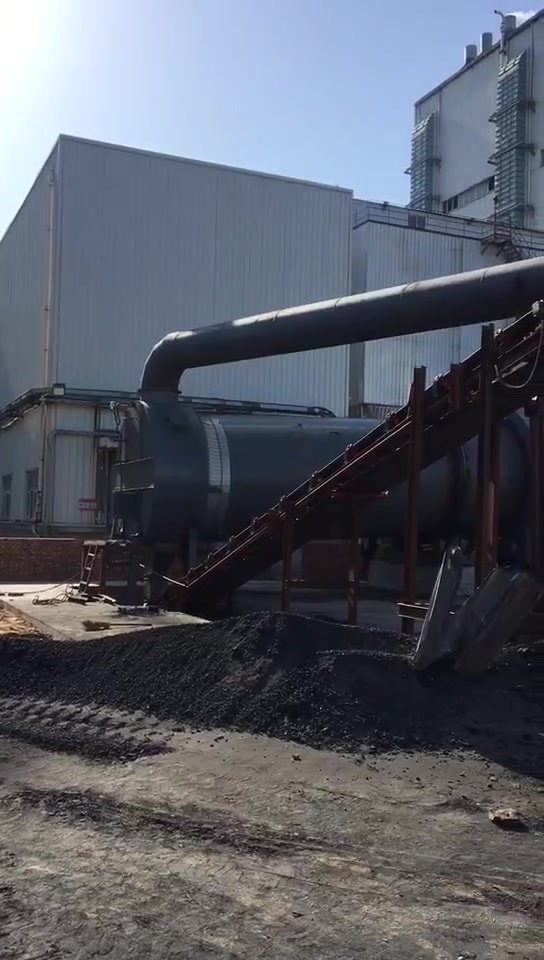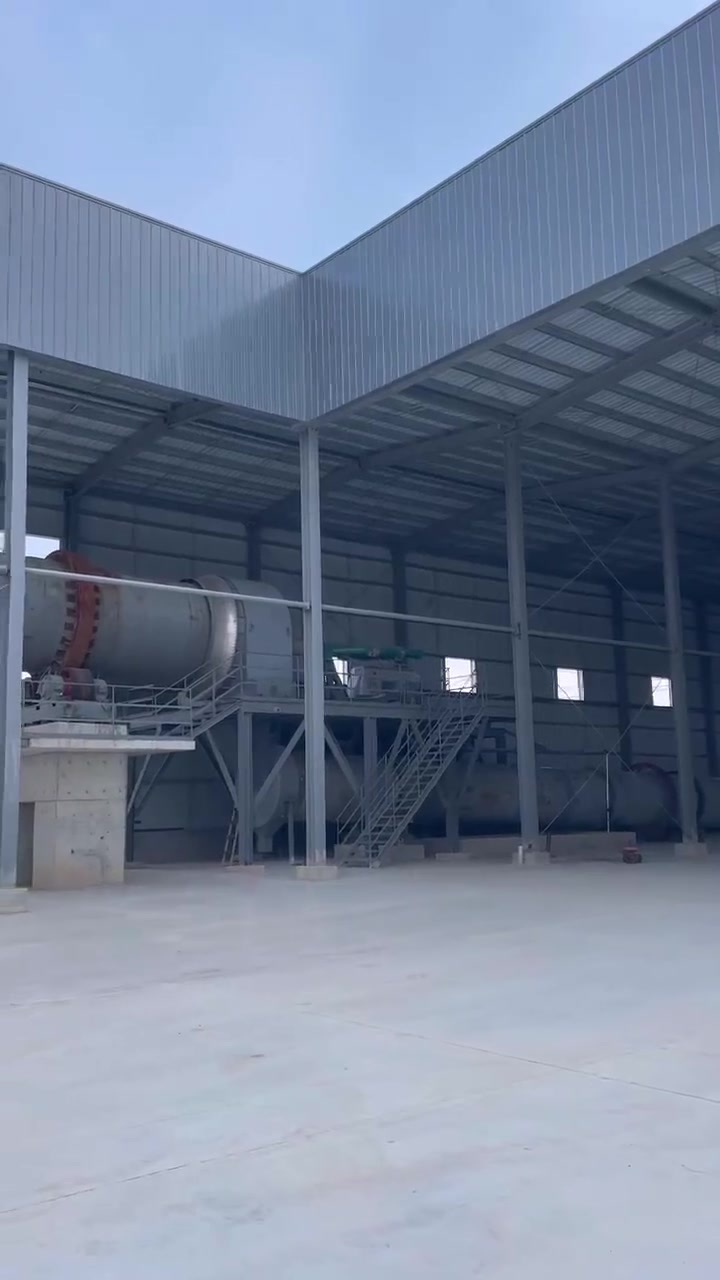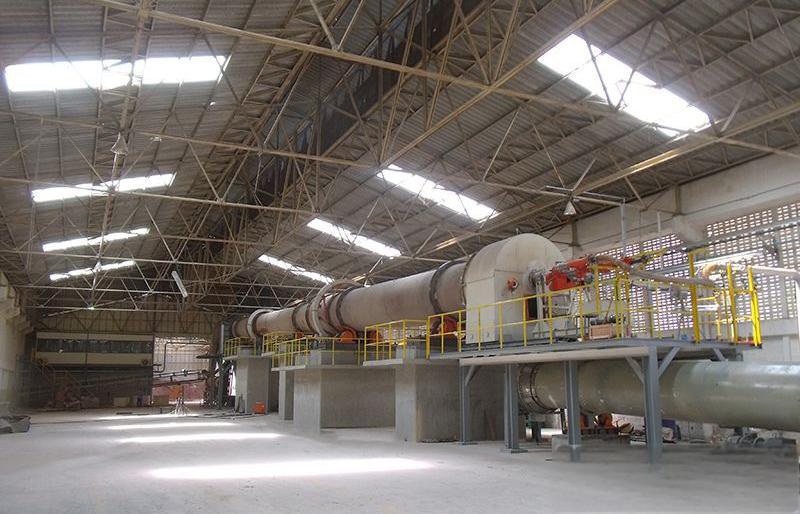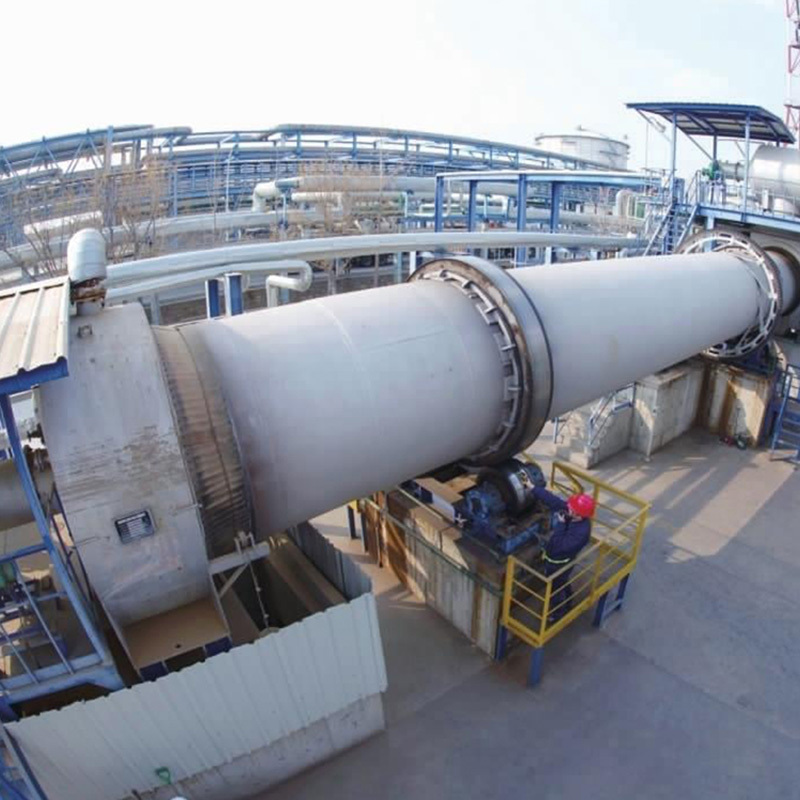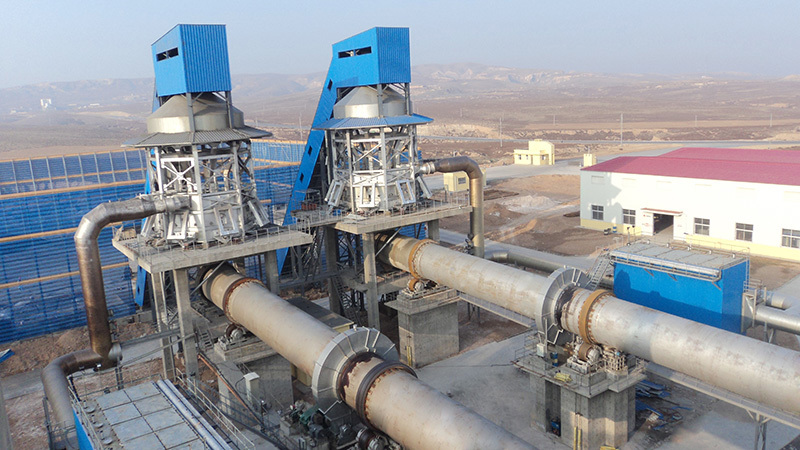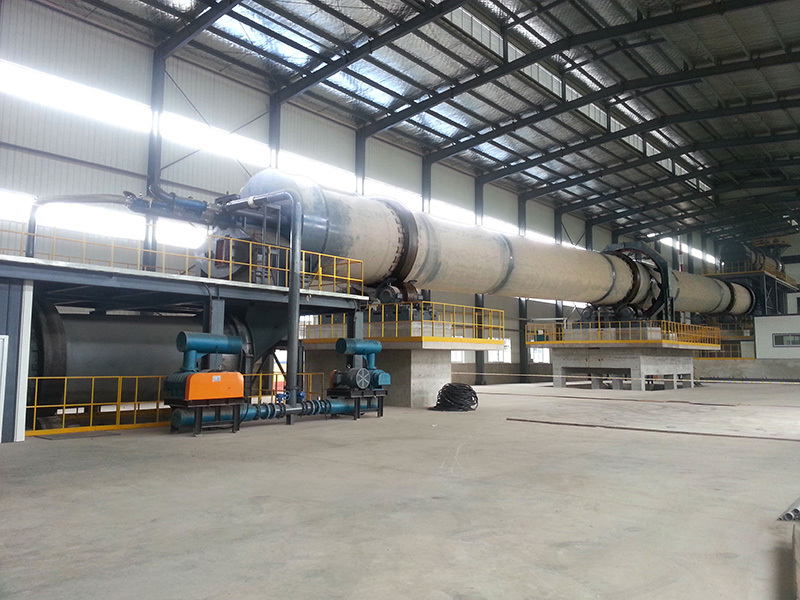
Lime rotary kiln
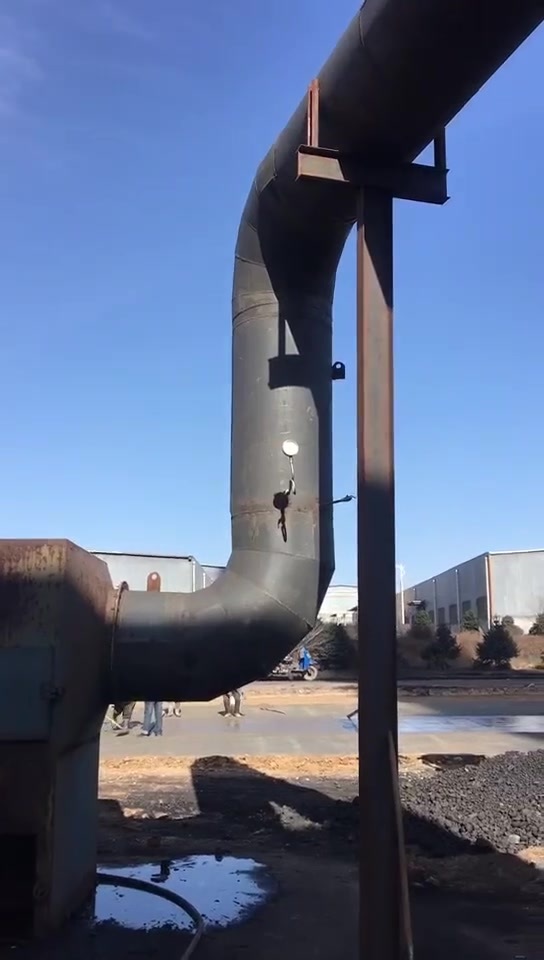
The energy-saving lime rotary kiln has a stable operation structure and adopts a low-pressure-loss vertical preheater to effectively improve the preheating effect. The decomposition rate of the preheated limestone before entering the kiln can reach 30%. It has strong fuel adaptability and can use solid powder fuel, liquid fuel and gas fuel. The finished lime has high activity. This type of kiln is widely used in the national steel industry, chemical industry, etc.
Excellent production
Excellent production
After-sales worry-free
Quality Assurance
Product Classification:
Rotary kiln
WhatsApp:+86-15038279844
Product Introduction
The rotary kiln is the most widely used kiln in the world for burning active lime, and is used in many production industries such as building materials, metallurgy, chemical industry, and environmental protection.
The energy-saving lime rotary kiln has a stable operation structure and uses a low-pressure loss vertical preheater to effectively improve the preheating effect. The decomposition rate of preheated limestone before entering the kiln can reach 30%; it has strong fuel adaptability and can use solid powder fuel, liquid fuel and gas fuel; the finished lime has high activity; this kiln type is widely used in the national steel industry, chemical industry, etc.

Technical features
1. The output of the rotary kiln is stable and suitable for large, medium and small active lime production lines.
2. The rotary kiln is an open calcination, with a simple kiln structure, smooth airflow, sulfur-containing flue gas can be discharged in time, and the sulfur in the fuel is not easy to adhere, so the product has a low sulfur content, which meets the requirements of steelmaking. At the same time, the material rolls forward evenly in the kiln, is heated evenly, the product quality is stable, the raw and overburning rates are very low, and high-activity lime for steelmaking can be calcined. Under the same conditions, the activity of lime produced by the rotary kiln is higher than that of the gas-fired kiln, with an average of more than 30mL, and the activity is generally 340-380mL, and even up to 400mL.
3. The rotary kiln can directly calcine 10-50mm fine-grained limestone. Generally, 0-30mm fine-grained limestone from mining products accounts for about 30-40% of the total output, and this part of limestone cannot be used by other kiln types. And with the "refined material" of steel raw materials, sintering gradually replaces limestone with quicklime, and fine-grained limestone cannot be comprehensively utilized. The construction of a rotary kiln production line can not only make full use of high-quality limestone mine resources, but also conform to the sustainable development policy of the lime industry.
4. The vertical preheater at the end of the kiln can make full use of the high-temperature flue gas generated by calcination in the rotary kiln to preheat the limestone from room temperature to the initial decomposition state. This can not only greatly increase the output of the rotary kiln, but also fully reduce the unit product heat consumption.
5. The vertical cooler at the head of the kiln can not only quench the high-temperature lime and increase the activity of the product, but also facilitate transportation and storage. At the same time, it can also obtain a higher temperature secondary air entering the kiln. It can effectively increase the firing temperature in the kiln and reduce fuel consumption.
6. The flue gas discharged from the vertical preheater at the end of the kiln has a low temperature and low dust content, making the subsequent flue gas treatment configuration simple and efficient, meeting environmental protection requirements.
7. The stable quality of the rotary kiln lime is its great advantage. Active lime production equipment is suitable for the comprehensive development of mining resources and has a good development prospect.
Process flow chart
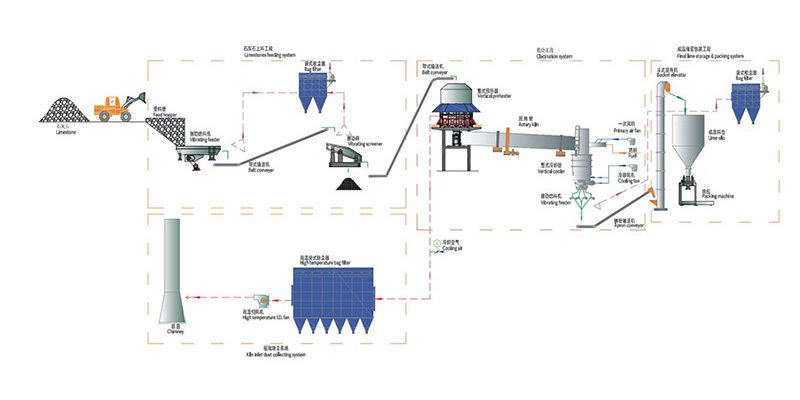
Typical production capacity main equipment configuration table
| Main Equipment | Capacity (t/d) | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| Main supporting equipment and technical and economic indicators | |||||||||||
| Vertical preheater | YRQ04 | YRQ06 | YRQ06 | YRQ06 | YRQOB | YRQ10 | YRQ12 | YRQ12 | YRQ14 | YRQ18 | |
| Rotary kiln | φ2.5×40m | φ2.8×43m | φ3.0×48m | φ3.2×50m | φ3.3×52m | φ3.6×55m | φ3.8×58m | φ4×60m | φ4.3×65m | φ4.9×70m | |
| Vertical cooler | LSF36 | LSF44 | LSF56 | ||||||||
| Calcination temperature/℃ | 1100±50 | ||||||||||
| Energy consumption index/(kCalkg lime) | 1200±100 | ||||||||||
| Power consumption index/(kW-h/t lime) | 40±5 | ||||||||||
| Limestone: Lime | 1.7~1.78:1 | ||||||||||
| Limestone transit rate/% | ≤5 | ||||||||||
| Lime activity/ml | ≥340(Specifically determined by the composition of limestone) | ||||||||||
| Ash discharge temperature/℃ | Ambient temperature +60 | ||||||||||
| Limestone kiln particle size/mm | 10~20/20~40 | ||||||||||
| Emission concentration/(mg/Nm³) | ≤30 | ||||||||||
| Number of working days per year | ≥340 | ||||||||||
| Overhaul cycle/year | 1~3 | ||||||||||
| Number of operators/(person/shift) | 2~3 | ||||||||||
| Applicable fuel | Pulverized coal, coke oven gas, blue coke furnace gas, converter gas, blast furnace gas, calcium carbide furnace gas, natural gas, diesel, heavy oil, liquefied petroleum gas, biomass fuel | ||||||||||
Note: This configuration table is for reference only and may vary depending on the customer's environmental geographical conditions and requirements.
| Serial number | Specification | Yield(t/h) | Speed(cpm) | Number of supports | Reducer | Electric Motor | kw | Remark |
| Model | ||||||||
| 1 | φ2.8×43m | 8.3 | 0.62-1.5 | 3 | Host ZS165-6 Auxiliary ZQ50-1 |
Host YCT355-4B Auxiliary Y160L-6 |
75 11 |
Preheater kiln |
| 2 | φ3.0×50m | 9.4 | 0.5-1.5 | 3 | Host ZS165-3 Auxiliary ZQ50-1 |
Host ZSN4-280-11B Auxiliary Y160L-6 |
125 11 |
Preheater kiln |
| 3 | φ3.2×50m | 10.4 | 0.4-1.5 | 3 | Host ZS130-16 Auxiliary ZQ50-10 |
Host ZSN4-280-11B Auxiliary Y180L-4 |
125 22 |
Preheater kiln |
| 4 | φ3.3×55m | 12.5 | 0.92-2.74 | 3 | Host NZS995-45VBL Auxiliary ZL42.5-10-2 |
Host ZSN4-280-11B Auxiliary Y160L-4 |
125 11 |
Preheater kiln |
| 5 | φ3.6×55m | 16.7 | 0.4-1.5 | 3 | Host ZSY500-40 Auxiliary ZSY180-31.5 |
Host ZSN-315-072 Auxiliary Y180L-4 |
250 22 |
Preheater kiln |
| 6 | φ3.8×58m | 20.8 | 0.4-1.5 | 3 | Host ZSY500-40 Auxiliary ZL50-14 |
Host ZSN-315-072 Auxiliary Y180L-4 |
250 22 |
Preheater kiln |
| 7 | φ4.0×60m | 25 | 0.4-1.5 | 3 | Host ZSY630-35.5 Auxiliary ZL65-16 |
Host ZSN4-355-092 Auxiliary Y200L-4 |
315 30 |
Preheater kiln |
| 8 | φ4.3×60m | 33.3 | 0.58-3.46 | 3 | Host JH560C-SW-63-1/2 Auxiliary ZL60-12-1/2 |
Host ZSN4-280-11B Auxiliary Y160L-6 |
2×125 2×11 |
Preheater kiln |
Active lime
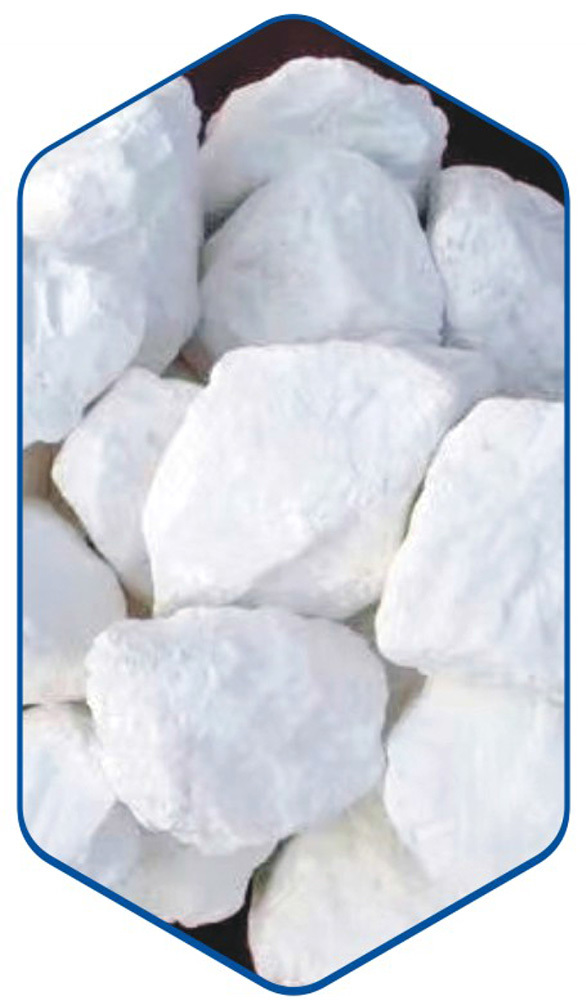

Lime, also known as quicklime or active lime, is mainly composed of calcium oxide. Active lime is mainly used as a "slag-making agent" for steelmaking, and is also widely used in environmental protection fields such as wet flue gas desulfurization and acidic industrial wastewater treatment, as well as chemical production processes such as light calcium carbonate, calcium carbide, briquette binder, epichlorohydrin, and sintered alumina. The activity of lime determines the activity of lime milk obtained in the lime digestion process, and the activity and concentration of lime milk determine the efficiency, purification degree and amount of waste gypsum slag of flue gas desulfurization and wastewater neutralization, and determine the quality of steel slag removal, light calcium carbonate, calcium carbide, alumina sinter and briquette binder, raw material utilization and operating costs.
Active lime production process
Active lime is mainly made of limestone, dolomite, chalk and other minerals with high calcium carbonate content, calcined at 1000-1100℃. There are many processes for the production of active lime, mainly including:
● "Preheater - Rotary Kiln - Vertical Cooling" Energy-saving Lime Production Process;
● Traditional "Long Rotary Kiln" Lime Production Process; Mixed-burning Vertical Kiln Lime Production Process;
● Gas-burning or oil-burning vertical kiln lime production process.
The choice of active lime production process is determined by many factors: investment cost, lime activity requirements, fuel selection, raw material particle size, system capacity requirements, and environmental protection requirements. We will determine the production process according to the specific situation and requirements of the customer.
Product Video
Key words:
Related Products
Related Products
Get Quote
Leave your contact information and get a free product quote
























